Education is a universal pursuit, but the way it is structured and delivered can vary greatly from country to country. The differences between education in China and in Western countries such as the United States or the United Kingdom are particularly notable. In this article, we will explore some of the key contrasts, while learning new words and phrases related to teaching and learning.
In China, the emphasis is often placed on rote learning, which refers to the memorization of information through repetition. Students are expected to memorize large amounts of content and reproduce it accurately in exams. This approach has its advantages, especially when it comes to subjects like mathematics, where formulaic knowledge is key. However, critics argue that it limits the development of critical thinking, a skill highly valued in Western education systems.

In contrast, many Western countries focus on fostering student-centered learning, a teaching method that encourages students to take an active role in their education. Here, teachers act as facilitators, guiding students through the learning process rather than simply presenting information. This method often involves project-based assignments and class discussions, promoting creativity and collaboration.
Another notable difference is the way assessment is conducted. In China, there is a strong focus on high-stakes exams like the Gaokao, a rigorous test that determines students’ future university prospects. Success in the Gaokao can shape a student’s career, making it one of the most important milestones in a young person’s life. Western countries, on the other hand, tend to use a combination of formative assessments, such as quizzes and assignments, alongside summative assessments, like final exams, to measure student progress throughout the year.
Additionally, the teacher-student relationship differs significantly between the two systems. In China, teachers are viewed as authoritative figures, and there is a clear hierarchy in the classroom. This contrasts with the more informal relationships in Western classrooms, where pedagogy often encourages open communication and even challenges to the teacher’s ideas.
Furthermore, the integration of technology in education is becoming increasingly important in both China and the West. In recent years, China has made significant investments in edtech, using tools like AI-powered learning apps to supplement classroom learning. Meanwhile, Western countries emphasize the importance of blended learning, a combination of traditional classroom teaching and online educational tools.
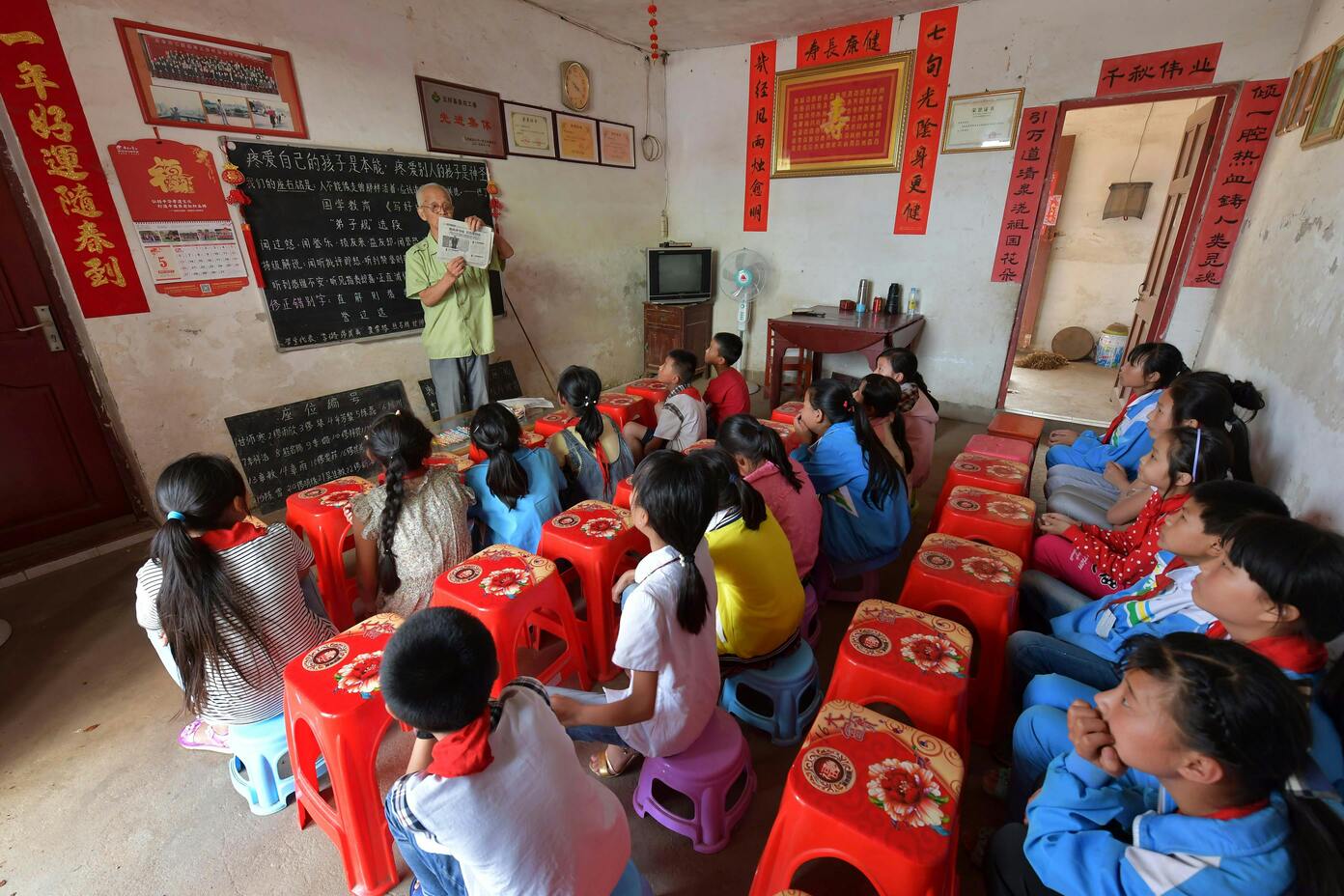

Ultimately, both systems have their strengths and weaknesses. While the Chinese system excels at building a strong foundation of knowledge through discipline and memorization, Western education tends to focus more on cultivating independence, problem-solving, and adaptability in students.
Vocabulary List and Explanation:
- Rote learning – A learning technique based on memorization through repetition.
- Formulaic knowledge – Information that is structured in a set or fixed way, often referring to facts or formulas that must be memorized.
- Critical thinking – The ability to analyze and evaluate information or arguments based on logic and reasoning.
- Student-centered learning – An educational approach that focuses on the needs, interests, and learning styles of the student, with the teacher acting more as a guide than a lecturer.
- Facilitator – A person who helps guide a process or discussion, in this context, a teacher who guides students in their learning.
- Assessment – The process of evaluating a student’s performance or understanding, often through exams or assignments.
- Gaokao – A high-stakes, national exam in China that determines university entrance.
- Formative assessment – A type of assessment designed to provide feedback to students and teachers during the learning process, helping improve learning outcomes.
- Summative assessment – A final evaluation at the end of an instructional period to determine if learning objectives have been met.
- Pedagogy – The art or science of teaching; education methods and principles.
These words and phrases are essential for understanding the different approaches to education in various cultures, particularly when comparing the systems in China and the West. By learning them, you’ll gain not only language skills but also insights into how teaching methods shape the way we learn and grow.